DISCO's Business Continuity Activities
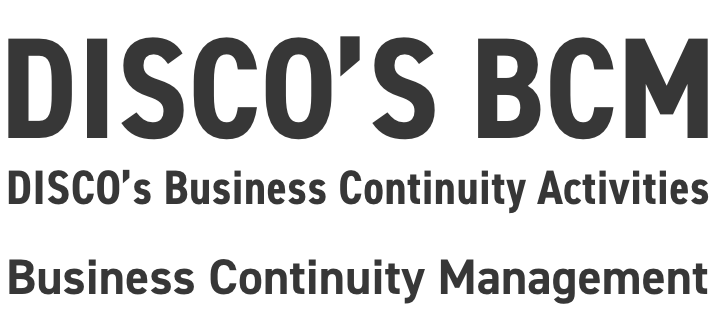
Establishing Systems that Support Stable Supply of Products and Grant our Customers a Sense of Security
During times of natural disasters, stagnation of our product supply can have an effect on our customers’ production.
DISCO has established a BCM (=Business Continuity Management) system in case of natural disasters such as earthquakes and unknown infectious diseases, so that customers can continue to use DISCO products with security.
Governance
At DISCO, important themes related to the company’s business continuity are assessed and resolved at the Executive Committee and Board of Directors. In addition, in 2004, a BCM Committee was established, with the Representative Director (currently denoted as Representative Executive Officer) acting as the chairperson, Executive Officers as members, and Outside Directors participating as observers. The BCM Committee is held every month, and BCM-related policies, goals for the fiscal year, direction of activities, etc. are assessed, and the progress of various measures are reported and discussed. In addition, “Risk response including BCM / management status” is composed by all the Outside Directors, and is one of the evaluation items for the Representative Executive Officer Evaluation Committee, a committee that evaluates the status of completion of the Representative Executive Officers. A designated organization in charge of BCM, the “BCM Operation Team” was also established, and they promote the establishment of BCM systems not only at the Head Office and the Haneda R&D Center, but also at all production sites including Hiroshima Works and Nagano Works.
Strategy
DISCO’s fundamental thoughts on risk management, stable supply, and BCM are stipulated in the Management Guidelines of our corporate philosophy, DISCO VALUES.

DISCO Group’s customers are part of a rapidly changing, high-tech industry, and are responsible for the supply of semiconductors and electronic components that support the world’s infrastructure. In such a business environment, the DISCO Group’s initiatives and systems toward stable supply have become one of the reasons why customers choose DISCO, and we believe that this added value is what sets us apart from other manufacturers in the industry, and will make the DISCO Group’s business more resilient and contribute to a sustained increase in our corporate value.
In addition, as mentioned above, our corporate philosophy, DISCO VALUES, states that “Business Continuity Management (BCM) is effective only when it has become a part of all daily work. The result will be demonstrated by our actions during times of emergency.” This represents our thoughts that in order to minimize the risks during an emergency such as a natural disaster or pandemic, it is not only important to implement tangible countermeasures such as facility investments, but also to ensure intangible countermeasures, such as promoting a BCM mindset and daily BCM-oriented behavior in employees, and achieving a state where being prepared for times of emergency is atarimae (“Atarimae” refers to the basics, common sense, normal, or matter of course in Japanese). By implementing the above, one of the goals of DISCO’s BCM countermeasures is for employees to not be dependent on just manuals or the instructions of the BCM Operation Team during times of emergency, but to aim for a state where each person and each department can make appropriate decisions and protect themselves from danger.
Based on this management policy, capital expenditure is strategically being used for the following main countermeasures.
1. Facility Investment and Countermeasures to Minimize the Impact of Risks
- Earthquake Countermeasures
- Countermeasures against Water Risks (including Ocean Hazards)
- Initiatives to Continue Production and Supply
- Countermeasures against Shipment and Transport Disruptions
- Information Security / IT-BCP
- Countermeasures against Infection Risks
Out of all natural disasters, Japan experiences frequent earthquakes, making earthquake countermeasures indispensable. Therefore, all factories that manufacture our main products adopt a seismically isolated structure, reducing the damage caused by earthquakes. In addition, DISCO also implements measures to procure electricity and prevent water risks.

1)Ocean hazards such as tsunamis and tidal waves
Kure Plant is located near the coast, and thus watertight walls and seawalls have been erected around the perimeter of the plant to mitigate the risk of tsunamis and tidal waves. The T.P. height of the seawall (height above sea level from Tokyo Peil (T.P.), the Japanese datum of leveling Tokyo Bay mean sea level) is designed to be 3.59 m high, and the structure of the seawall at the entrance of the factory (refer to photographs below) has been made such that it automatically rises when water is detected during a disaster. In addition, the main production facilities are located on the 2nd floor and above in order to minimize the impact from water risks, and a watertight door has been installed to protect important facilities on the 1st floor as well.
Seawall at the entrance of the factory
(Normal state)

(Seawall when up)

Height of sea level and Kure Plant's design
2) Water outage risks
At Kuwabata Plant, a system where approx. 1,000 t of industrial water can be stored underneath the plant and used to continue production for approx. 10 days in a water outage has been established. In addition, a well water pump that can be used to collect groundwater has also been established, further preparing against water outage risks.
A priority level has been assigned to each product type, detailed recovery objectives in times of disaster have been set, and the following countermeasures are in place.

1) Precision processing tools
Out of all our product categories, as a stop in supply of our precision processing tools (blades and wheels) would have the largest impact on our customers’ production, precision processing tools are given the highest priority in terms of recovering production, and measures such as the stockpiling of raw materials necessary for production and reduction of procurement risks are being implemented.
・Stockpiling of raw materials
In preparation for a disruption in the supply chain or suspension of raw material supply due to disasters, a minimum of 6 months or more of inventory (raw materials) is stockpiled at all times.
・Countermeasures against procurement risks
DISCO carefully assesses the few hundred supply sources that are selected upon taking regional risks and the frequency of occurrence of these risks into account, and performs risk evaluations for the procured products. Measures such as prioritizing and stockpiling a larger amount of procured products that have higher risks are in place.
・Establishment of an alternative production system
DISCO is promoting the establishment of a system that aims to achieve production of the same precision processing tool products at two different manufacturing sites, Hiroshima Works (Kure Plant, Kuwabata Plant) and Nagano Works (Chino Plant).
Ultimately, the goal is to achieve production at two manufacturing sites for all products. The purpose of this system is to be able to continue supplying products to our customers by having another manufacturing site as backup in the event that production stops at one manufacturing site.
・Stand-alone manufacturing main system
・Hedging against risks by decentralizing storage locations
Equipment maintenance parts are not only stockpiled at DISCO, but also at external warehouses. This system enables DISCO to continue providing our customers with products even if one of the locations suffers damage due to a disaster.
・Establishment of a department dedicated to parts supply as part of the Sales Division
A department dedicated to parts supply has been established as part of the Sales Division, and a system has been prepared such that risk countermeasures and support in times of emergency can be carried out consistently.
・Stockpiling of both raw materials and completed products
In preparation for a disruption in the supply chain or suspension of raw material supply due to disasters, a few months or more of inventory (raw materials) is maintained at all times. In addition, by also maintaining inventory of completed products, a system where product supply can be continued even if a sudden raw material supply suspension were to occur has been established.
・Preparation for a stop in water supply
Water solution products use a large amount of water resources during the manufacturing process, and can have a large impact on production if water supply were to stop. To prevent this, DISCO has established countermeasures against water outages.
・Shipment of completed products during disasters
By securing a backup power supply for inspection devices, a system where shipment of completed products can be resumed within 3 days after the disaster has been established.
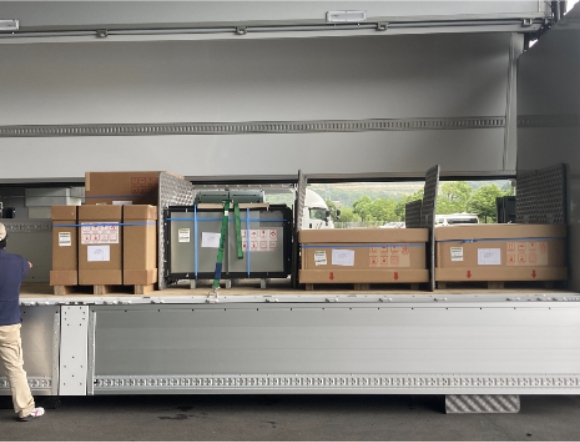
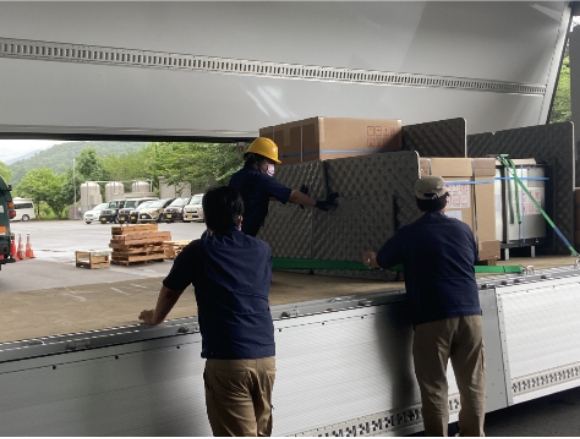
1) Alternative transport using a DISCO-owned truck
DISCO owns a 10 t heavy truck with a max. payload capacity of 6.5 t or more, and establishes a system that allows DISCO-facilitated transport of products during disasters that disrupt shipping company operations. In addition, this alternative transport system is periodically carried out as practice and tested.


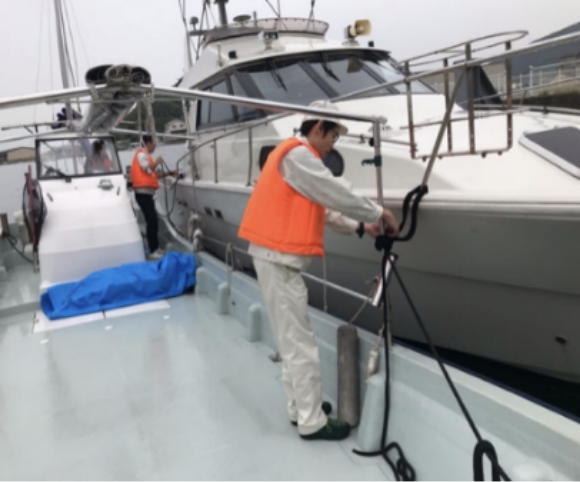
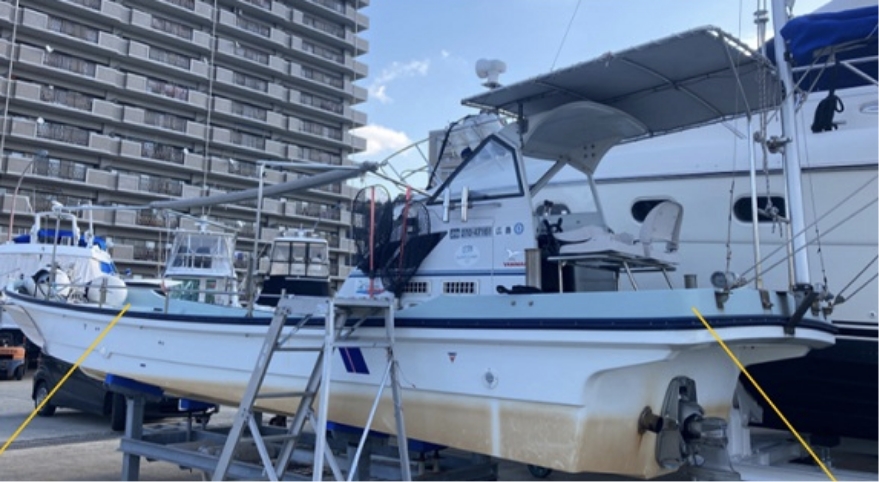
DISCO is performing verifications of transport using a chartered boat, etc. as a countermeasure in the event that land routes are blocked. In addition, a system that allows sea transport using a DISCO-owned boat has also been established.


In recent years, cyberattacks have been increasing globally, with threats such as cyberterrorism via computer viruses, large-scale information leaks, and business email fraud becoming more serious. In preparation for such threats and from the perspective of business continuity, the DISCO group has implemented the following measures.
i) Information Security Management System
1. Responsible OfficersWe regard information security and the protection of personal information as key management issues. The Representative Executive Officer and President serves as the Chief Information Officer (CIO), while the Managing Executive Officer is appointed as the Chief Privacy Officer (CPO). Strategies and concrete development plans related to information systems are determined annually at management meetings.
2. Policies and Rules
We have established policies, regulations, and guidelines regarding information security and the handling of personal information. These are continuously communicated and taught to all executives and employees to ensure compliance. If any violations of these rules are found, appropriate disciplinary actions are taken in accordance with the Rules of Employment and other internal rules.
3. Internal Audits
We conduct internal audits on information security and personal information protection once a year to continuously strengthen and improve our management framework.
4. Escalation System
We have established channels to carry out consultations, proposals, reporting, or whistleblowing for matters related to information security and personal information.
*Note: These channels also accept consultations and reports related to acts or potential acts that violate ethical standards or compliance.
5. Operation Based on International Standards
We strive to continuously improve our security level by referring to the U.S. security standard “NIST SP 800-171.”
ii) Initiatives to Strengthen Information Security
1. Isolation of Core Manufacturing Systems at Each Manufacturing SiteThe core systems at each manufacturing site are designed to operate independently without inter-site connectivity, ensuring that disruptions caused by virus infections or similar issues do not spread to other locations.
2. Review and Update of Incident Response Measures
To address increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, we have developed an information security plan that includes incident response procedures for security incidents, including preparation, detection, analysis, response, and recovery. We inspect and revise this plan at least twice a year.
3. Vulnerability Assessments by Third Parties
In order to objectively evaluate our information security measures, we conduct security risk assessments and vulnerability analyses through external organizations. Based on the results, we implement continuous improvements.
4. Information Security Training
In addition to onboarding training, all employees—including full-time, fixed-term, part-time, and dispatch employees—receive annual information security training.
We also conduct targeted email training, and the results are shared company-wide to raise awareness and support future countermeasures.
To prepare for disasters such as earthquakes, we have implemented the following additional measures.
5. Inter-site Server Backup System
We have developed a system for backing up servers between locations so that business operations can continue even if a server at one site goes down. The IT department and all departments regularly verify this system to ensure smooth switching between servers.
6. Redundancy of Internet Connections at Manufacturing Sites
We have implemented redundancy for the internet connections at each manufacturing site by separating the incoming routes in order to ensure network stability.
DISCO has been taking countermeasures against the spread of the new-type influenza since June 2008. The DISCO group as a whole has been preparing for pandemics with the three following policies: “Not to let even a single employee become infected,” “not to spread the infection if any employee becomes infected” and “to establish a system for business continuity to meet the situation.” Even during normal times, for example, all employees measure their temperature every day before coming to work, and disinfect their hands upon entering the company. We have also prepared stockpiles of masks and disinfectant solutions.
2. Framework of Business Continuity Activities
- Assuming the Occurrence of Disasters and Analyzing the Impact on Business
- Framework of BCM Activities
- Supplier risk management
- Acquisition of External Certification (ISO22301:2019 certification)
DISCO assumes the occurrence of risks that may hinder business continuity and the occurrence scale of these risks, and investigates and analyzes the impact of these assumed risks (earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, heavy rains, heavy snow, other natural disasters, accidents such as fires and explosions, conflicts such as terrorism and political disturbances, widespread contagious diseases, infectious diseases, etc.) on business continuity and resuming operations.
Based on the policies and fiscal year targets formulated by the BCM Committee, company-wide activities, such as the implementation of various countermeasures, are carried out for the sake of business continuity. In addition, at the BCM Committee, 40 departments that possess functions necessary for business continuity are selected to be part of a “BCP applicable organization,” and focused BCM countermeasures are carried out every year for these applicable departments based on the PDCA cycle shown below.
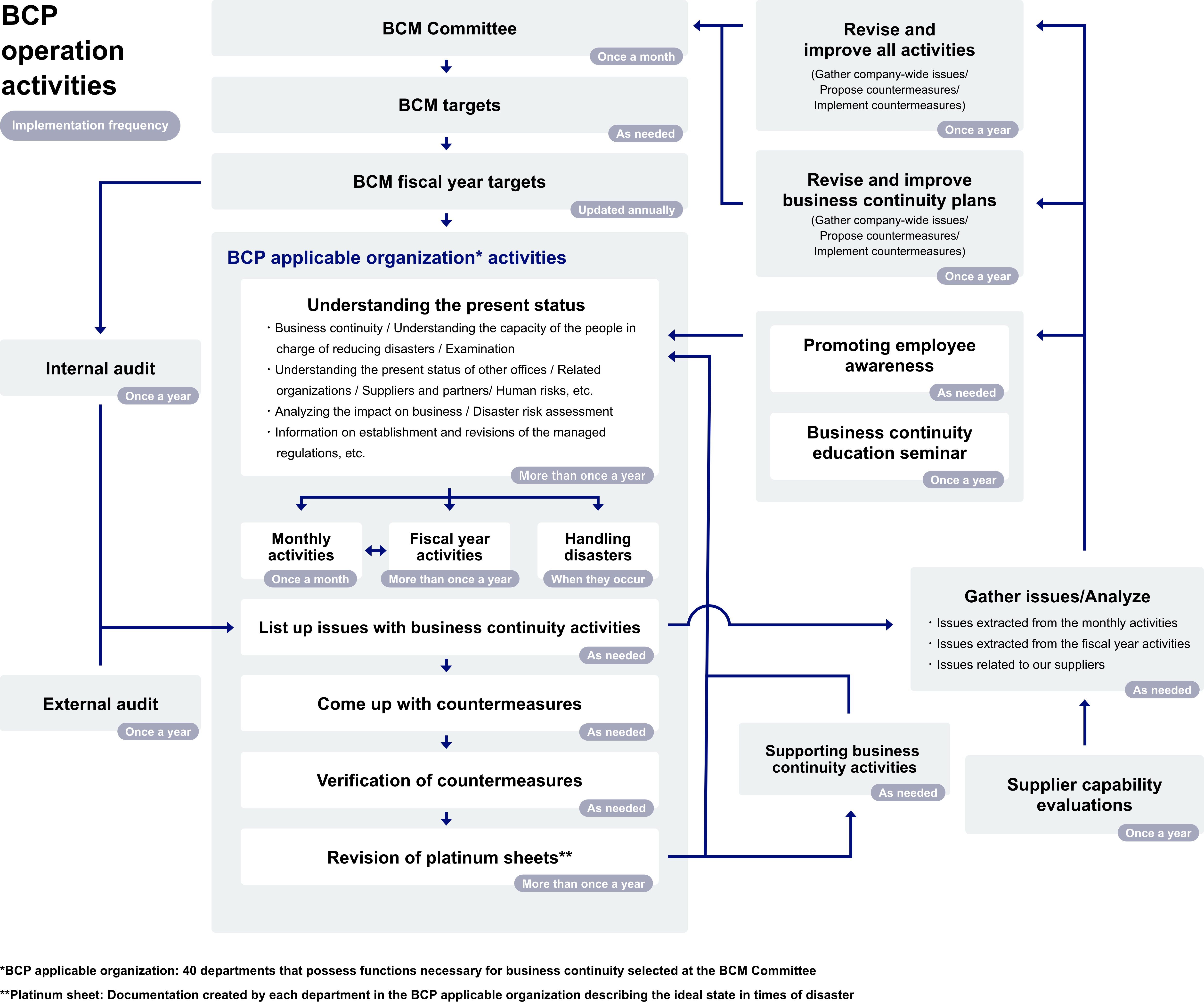
1) Monthly activities
Each department in the BCP applicable organization performs monthly activities where countermeasures against the risks related to business continuity are carried out and reported. The details of the activities are reported to the BCM Committee every month, and good examples are shared at the General Managers Meeting with all Division Managers in attendance, and implemented and shared across the entire company.
Example 1. Export Control Office
In preparation for a situation where land routes are blocked, they established a sea transport system that uses a chartered boat or regular ferry routes, and verifications are being performed.
Example 2. Accounting Department
The Accounting Department at the Head Office and Hiroshima Works take turns handling the payment procedures every month and can immediately back each other up in times of emergency such as during a disaster, establishing a system that enables smooth payment procedures.
From the reports of the monthly activities, the BCM Operation Team extracts and analyzes the risks that are recognized by each department, sets fiscal year activities for risks that are commonly recognized by multiple departments, and carries out these common activities for all departments in the BCP applicable organization. Through this, DISCO aims to implement cross-departmental countermeasures before the risks become larger and strengthen danger prevention measures.
DISCO carries out supplier capability evaluations once a year, and monitors the business continuity system of our suppliers. In addition, if the results of the evaluation show a low score for an important supplier, we visit them and provide seminars on BCM countermeasures.
DISCO has acquired the ISO22301:2019 certification through an external certification body with the aim of receiving recognition that our BCM activities are adequate from an objective perspective. In 2008, DISCO was the first semiconductor-related company in Japan to acquire the BS25999 certification, and in 2012, DISCO was the first Japanese company to acquire the ISO22301 certification. In addition, DISCO has continued to undergo audits from external certification bodies for ISO22301 once a year since its acquisition, and continues to maintain the certification.
3. Improving Employee Awareness
- Education
- Employee Incentives
Undertaking a BCM education seminar is mandatory for new employees and mid-career employees when they join the company, and DISCO is promoting understanding of the company’s countermeasures, behavior expected of employees, etc.
For example, DISCO provides incentives based on each employee’s BCM countermeasure implementation status, such as measuring their temperature every day, stockpiling supplies for their house in preparation for times of disaster (food, water, daily essentials, etc.), not placing items that may fall over in case of an earthquake in the bedroom, etc. These are counted as points, and these points are reflected to a portion of each employee’s bonus.
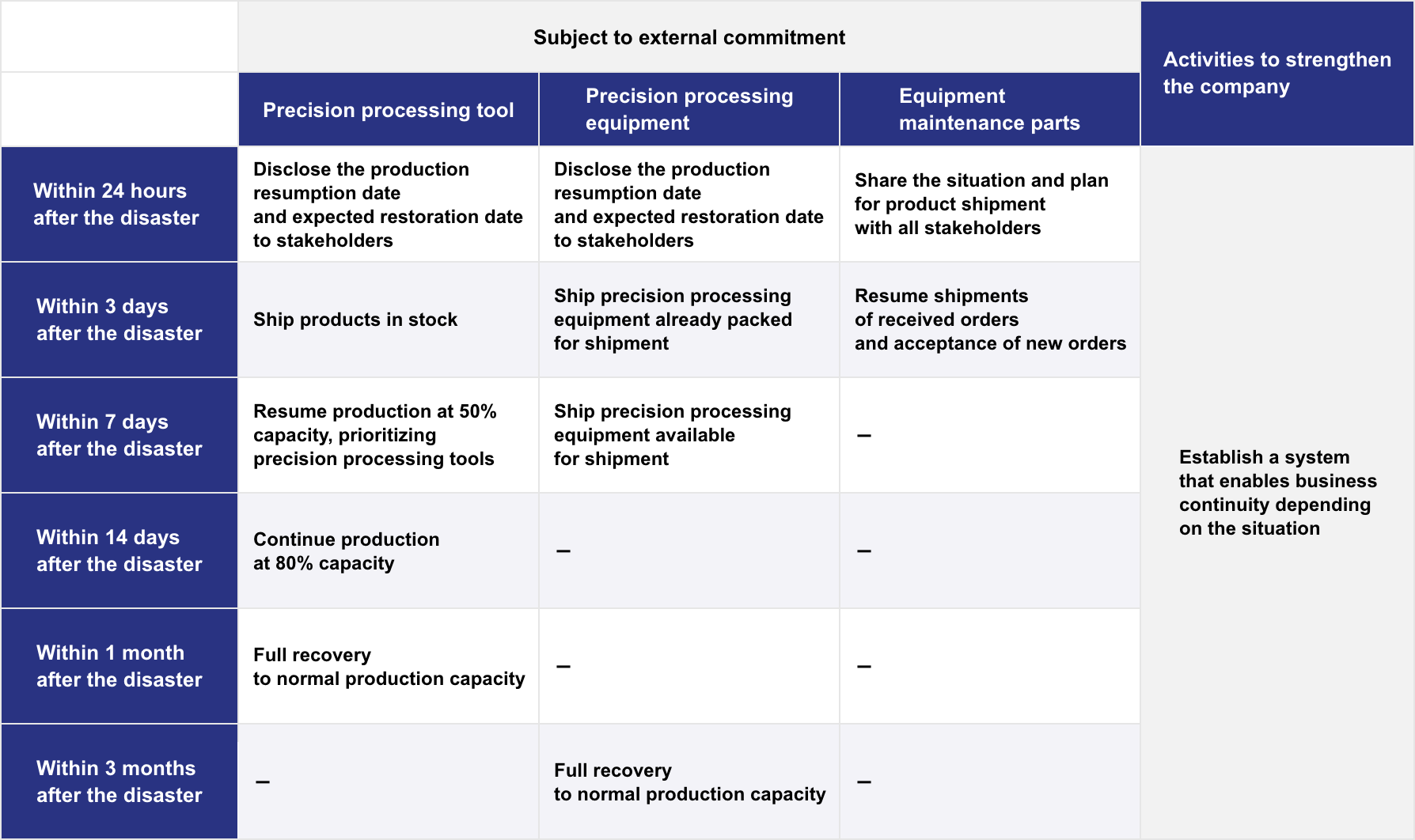
Metrics and Targets (DISCO’s Recovery Objectives in Times of Disaster)
DISCO has set and disclosed recovery target times for areas of our business such as the manufacturing and shipment of precision processing tools and equipment, and receiving orders for equipment maintenance parts in the case where DISCO is affected by a disaster.
We believe that clarifying and disclosing our business continuity objectives will grant our stakeholders with a feeling of security.
A system to maintain and improve BCM
DISCO has established a management system compliant with ISO22301:2019 in order to maintain and continue to improve the company’s BCM.


